The Many Faces of Ika Protocol
An interoperability solution? A Zero Trust privacy solution? An MPC solution? A distributed wallet? Ika Protocol is building key primitives that allow for a variety of solutions to be used together or separately across chains.
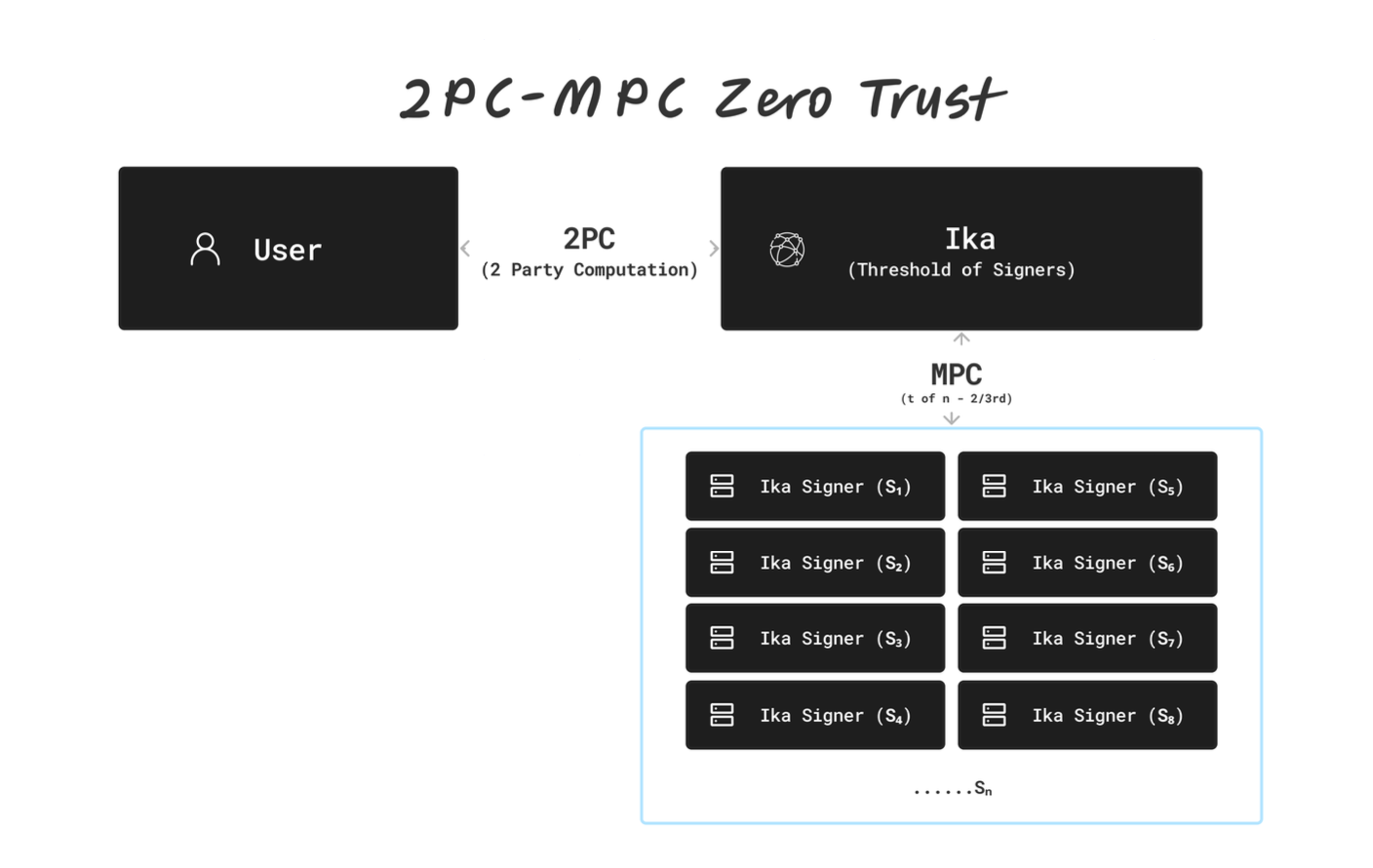
Ika is a decentralized, high-performance, and secure blockchain interoperability solution built on the 2PC-MPC (Two-Phase Commit Multi-Party Computation) protocol. The project aims to overcome key challenges in cross-chain communication, including security risks, performance bottlenecks, and decentralization constraints. By utilizing Zero Trust cryptography and Sui’s Mysticeti, a DAG-based Byzantine consensus protocol, Ika ensures trustless, scalable, and low-latency blockchain interactions.
Key Problems in Blockchain Interoperability
- Security risks: Traditional solutions like cross-chain bridges and federated MPCs introduce vulnerabilities, including collusion attacks and honeypots.
- Performance issues: Existing interoperability solutions suffer from high latency and low throughput, limiting real-time cross-chain operations.
- Decentralization challenges: Many current models rely on a small number of validators, undermining blockchain’s core principles.
- Trust dependencies: Solutions often require centralized custodians or intermediaries, contradicting the ethos of decentralization.
Ika’s Solution: The 2PC-MPC Protocol
The 2PC-MPC protocol enhances security, efficiency, and scalability by integrating:
- Decentralized key management: Private keys are split into cryptographic shares, ensuring no single party has full control.
- Presignature mechanism: Reduces signing delays by precomputing cryptographic operations.
- Threshold homomorphic encryption: Ensures secure multiparty computations without exposing private key fragments.
- Mysticeti’s broadcast communication: Replaces traditional unicast messaging with a DAG-based protocol, improving scalability.
- Asynchronous and fault-tolerant architecture: Allows seamless network participation even under failures.
dWallets: A New Decentralized Primitive
Ika introduces dWallets, programmable blockchain accounts controlled by decentralized MPC networks. Key features include:
- Smart contract integration: dWallets can be programmatically controlled by smart contracts for automated transactions.
- Dynamic participation: Nodes can join or leave without disrupting network operations.
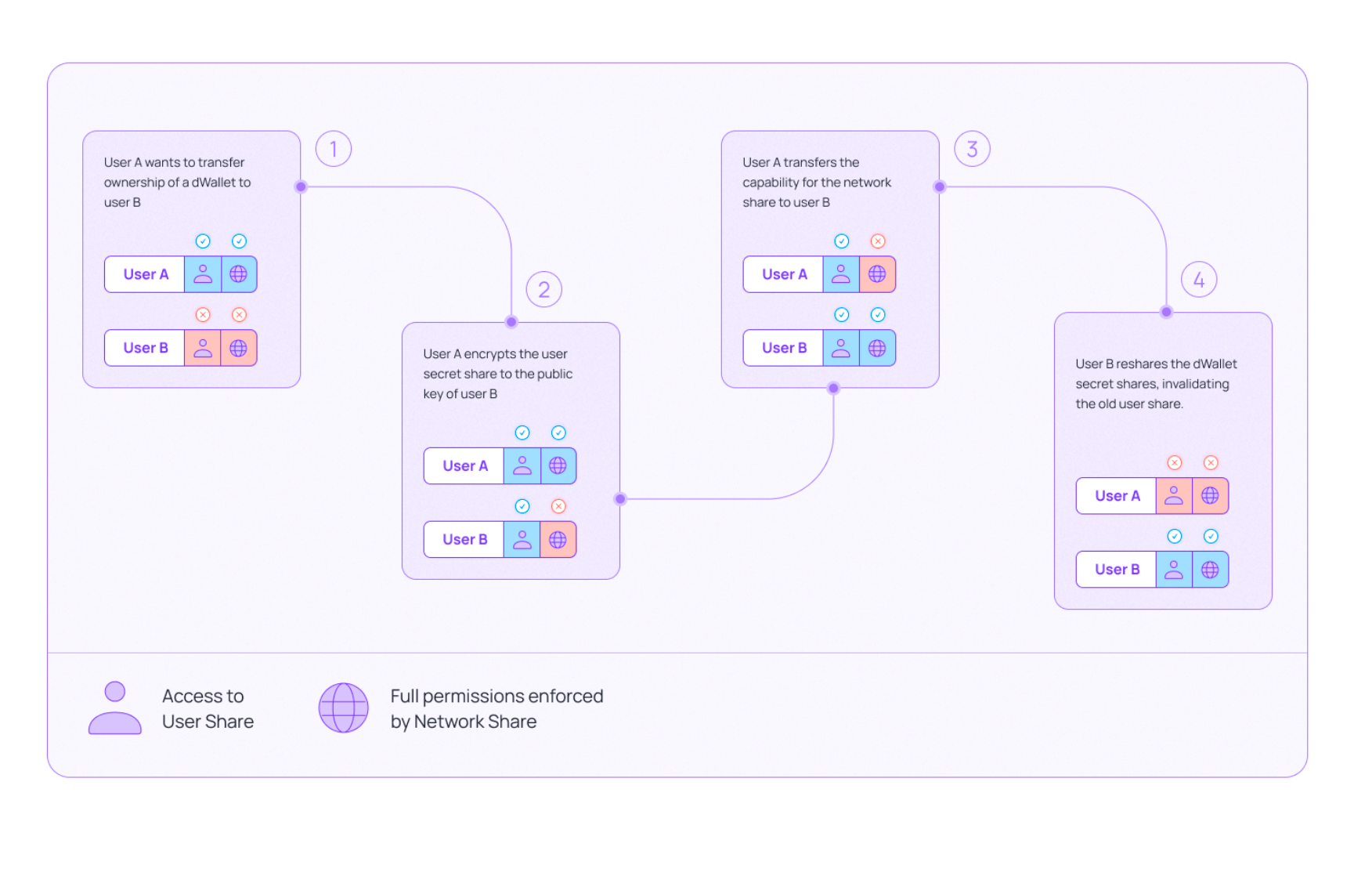
- Transferability: dWallets can be transferred securely between users or DAOs, unlocking novel use cases.
Transferability is particularly an interesting novel primitive since it allows custody of wallets to be transferred. Note the difference between User A sending wallet balances to User B versus User A selling the wallet itself. This allows for interesting novel use cases in DeFi lending, where the collateral balance can be all the assets on the wallet balance, the lending protocol would have a better understanding of the user’s credit risk. It also facilitates handling of illiquid assets such as NFT’s; a wallet with a collection of NFT’s could put up the wallet/collection itself for sale as opposed to having bids placed individually in an illiquid market.
Other Use Cases
- Decentralized finance (DeFi): dWallets enable cross-chain liquidity, automated trading strategies, and secure custody.
- Gaming & NFTs: Facilitates programmable asset ownership, secure transfers, and cross-platform interoperability.
- Institutional & enterprise adoption: Supports multi-signature approvals, secure fund disbursement, and cross-border payments.
- DAOs & governance: Enables multi-chain treasury management and trustless execution of governance decisions.
- Multi-chain atomic swaps: Secure and trustless asset swaps without intermediaries or wrapped tokens.
- Retail custody solutions: Protects users from key loss and security breaches with programmable recovery mechanisms.
Security & Governance Model
- Cryptographic security: Built on threshold homomorphic encryption, Zero Trust MPC, and secure multi-party ECDSA signing.
- Economic security: Uses a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) model, where signers stake IKA tokens to ensure honest participation.
- On-chain governance: Token holders can vote on protocol upgrades, fee structures, and economic adjustments.
Conclusion
Ika’s 2PC-MPC (Two-Phase Commit Multi-Party Computation) enhances decentralized signing by improving efficiency, security, and scalability. Traditional MPC methods face issues with network congestion and centralization, but Ika’s innovation allows thousands of nodes to operate securely in parallel, reducing delays and vulnerabilities. By leveraging broadcast communication and a zero-trust architecture, it ensures trustless, tamper-proof cryptographic signing for blockchain applications, benefiting DeFi, cross-chain interoperability, and decentralized custody.

